Overview Table
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Common Issue Name | WiFi Connected but No Internet |
| Affected Devices | Windows PCs, laptops, smartphones, tablets |
| Network Type | Home WiFi, office networks, public hotspots |
| Typical Symptoms | Internet not working despite WiFi connection |
| Main Causes | Router issues, ISP problems, IP conflicts, DNS errors |
| Skill Level Required | Beginner to Advanced |
| Time to Fix | Few minutes to several hours |
| Data Loss Risk | None |
| Long-Term Solution | Network optimization and regular maintenance |
Introduction
Seeing the Fix WiFi Connected but still being unable to access the internet is one of the most confusing and frustrating connectivity problems. The device appears online, the signal strength looks strong, and yet web pages refuse to load, apps fail to sync, and online services remain unreachable. For many users, this situation raises immediate doubts about their device, their router, or even their internet service provider.
This issue is more common than most people realize. It affects home users, office environments, and even enterprise networks. The problem lies in the fact that Fix WiFi Connected and internet access are not the same thing. WiFi only represents a local wireless connection between your device and a router. Internet access requires that router to successfully communicate with external servers through your ISP.
This guide explains how to fix the “WiFi connected but no internet” issue in a structured, logical, and practical manner. The approach blends narrative clarity, analytical reasoning, technical depth, and journalistic explanation to help you understand not just the solutions, but the underlying mechanics of the problem.
Understanding the Difference Between WiFi and Internet
What WiFi Connection Really Means
When your device shows that it is Fix WiFi Connected, it simply means that a wireless link has been established between your device and a router or access point. This connection is local and does not automatically guarantee internet access.
How Internet Access Works
For internet access to function, several components must work together:
- The router must receive data from your ISP
- The modem must authenticate with the ISP network
- DNS servers must translate domain names into IP addresses
- Your device must receive valid network configuration details
If any of these steps fail, you may remain connected to Fix WiFi Connected without actual internet connectivity.
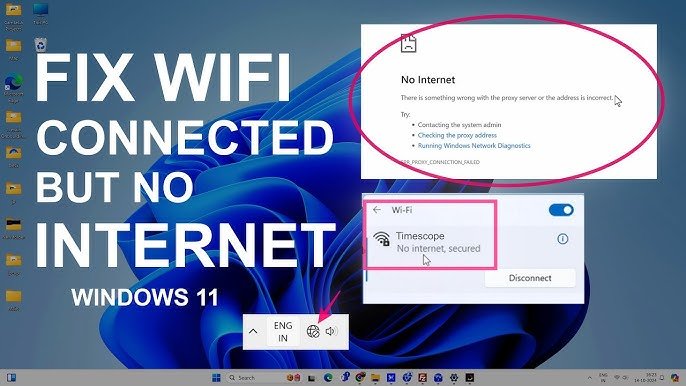
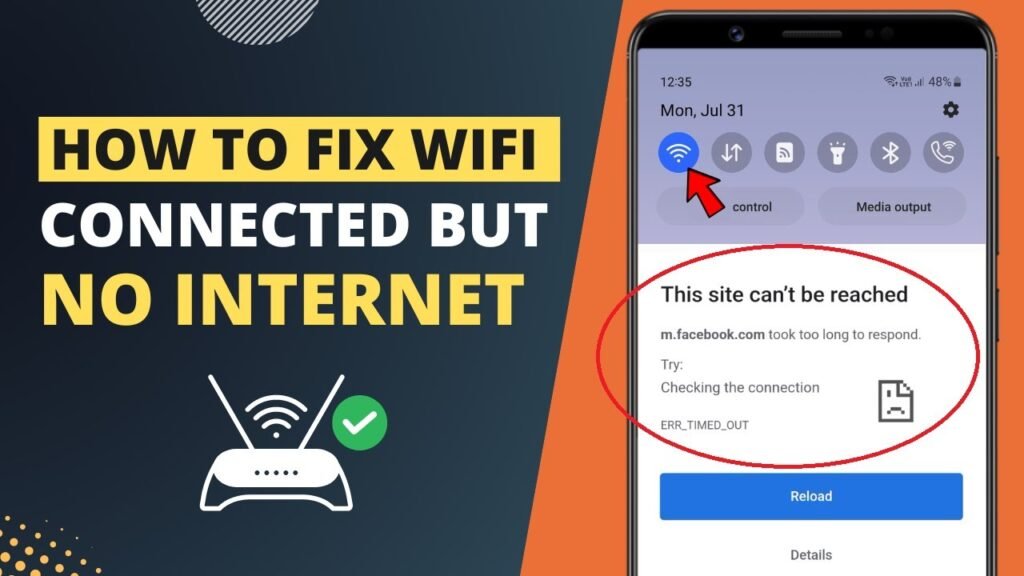
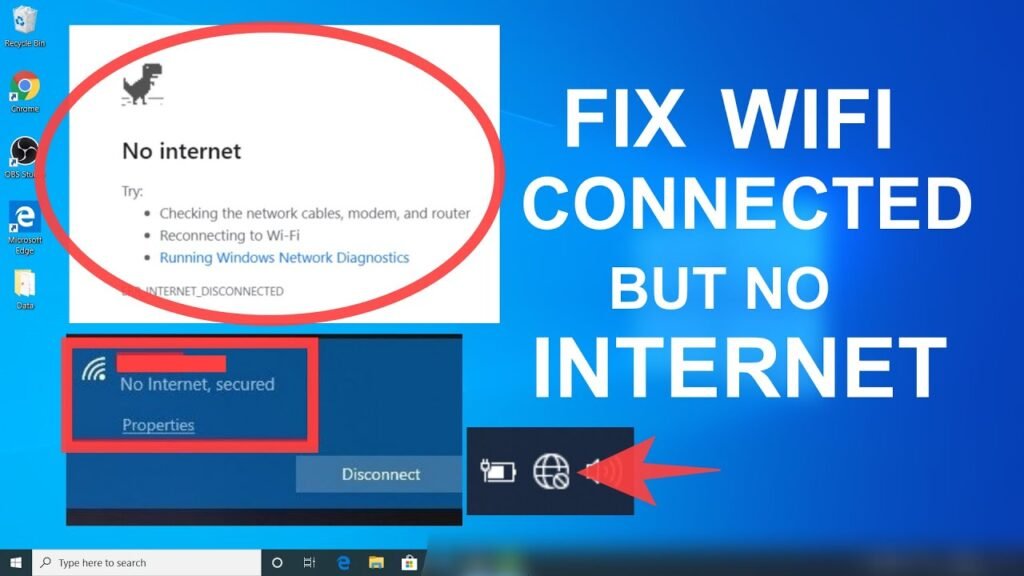
Common Symptoms of WiFi Connected but No Internet
Web Pages Fail to Load
Browsers may display error messages indicating that the site cannot be reached or that DNS resolution failed.
Apps Show Offline Status
Messaging apps, cloud services, and streaming platforms may stop updating or syncing.
Limited Connectivity Warnings
Some devices show messages such as “No internet access” or “Limited connection” despite being connected.
Internet Works on Some Devices but Not Others
This indicates that the problem may be device-specific rather than network-wide.
Initial Checks Before Deep Troubleshooting
Verify the Internet Service Status
Sometimes the issue is not inside your home or office at all. Temporary ISP outages, maintenance work, or regional disruptions can cause internet loss while Fix WiFi Connected remains active.
Test Another Website or App
A single website failure does not always indicate a network issue. Try accessing multiple sites or services.
Restart the Affected Device
Temporary software glitches, memory issues, or background process errors can interrupt internet access.
Restarting Network Equipment Properly
Why Restarting Works
Routers and modems manage continuous data streams. Over time, memory leaks, software bugs, or connection overloads can disrupt communication.
Correct Restart Sequence
Turn off the modem first, then the router. Wait for at least one minute before turning the modem back on, followed by the router.
Testing After Restart
Once devices reconnect, test internet access again before proceeding to advanced steps.
Checking Router and Modem Indicators
Understanding Status Lights
Most networking devices use indicator lights to show connection status. These lights provide clues about whether the router is receiving internet data.
Identifying Connection Failures
If the internet or WAN light is off or blinking abnormally, the issue may lie between the modem and ISP.
Ethernet Cable Inspection
Loose or damaged cables between the modem and router can disrupt internet flow while Fix WiFi Connected remains active.
Verifying Network Configuration on Your Device
IP Address Assignment
Devices require a valid IP address to access the internet. An incorrect or missing IP address prevents data routing.
Automatic vs Manual Configuration
Ensure that IP and DNS settings are set to automatic unless you intentionally configured them manually.
Renewing Network Configuration
Disconnecting and reconnecting to Fix WiFi Connected forces the device to request fresh network settings.
Checking DNS Settings and Failures
What DNS Does
DNS converts website names into numerical IP addresses. Without proper DNS resolution, the internet becomes inaccessible.
Symptoms of DNS Issues
Websites fail to load while IP-based connections may still work.
Switching DNS Temporarily
Using alternative DNS configurations can help confirm whether DNS is the root cause.
Disabling and Re-enabling Network Adapters
Why This Helps
Network adapters sometimes enter unstable states due to driver glitches or power management conflicts.
Resetting the Adapter
Disabling and re-enabling the adapter forces it to reload drivers and renegotiate the connection.
Testing After Reset
Check internet access immediately after reactivation.
Updating or Reinstalling Network Drivers
Role of Network Drivers
Drivers enable communication between the operating system and network hardware. Faulty drivers can block internet traffic.
When Driver Issues Occur
Driver problems often appear after system updates, hardware changes, or prolonged uptime.
Reinstallation Benefits
Reinstalling drivers replaces corrupted files and resets configuration parameters.
Checking Proxy and VPN Settings
How Proxies Affect Internet Access
Incorrect proxy settings can redirect traffic to unreachable servers.
VPN Connectivity Issues
VPN services may connect successfully but fail to establish a secure tunnel, blocking internet access.
Temporary Disable Test
Disabling VPN or proxy settings helps identify whether they are causing the issue.
Firewall and Security Software Interference
Security Software Behavior
Firewalls and security tools monitor and filter traffic. Misconfigured rules can block legitimate connections.
Identifying False Blocks
If internet access resumes after temporarily disabling security software, configuration adjustments are needed.
Restoring Secure Access
Never leave security software disabled permanently. Adjust rules instead.
Flushing Network Cache and Resetting Protocols
Why Cache Can Cause Problems
Network cache stores temporary data that may become outdated or corrupted.
Resetting Network Protocols
Resetting network stacks clears internal errors and restores default behavior.
System Restart Requirement
Most protocol resets require a system restart to take effect.
Testing Internet Access Using Ethernet
Why Ethernet Testing Matters
Wired connections bypass Fix WiFi Connected related issues, helping isolate the problem.
Interpreting Results
If Ethernet works but Fix WiFi Connected does not, the issue lies in wireless settings or hardware.
Router Wireless Configuration Review
Check Fix WiFi Connected channel settings, encryption methods, and firmware stability.
Checking Router Firmware and Configuration
Importance of Firmware Stability
Router firmware controls traffic routing, security, and device compatibility.
Firmware Update Benefits
Updates fix bugs, improve compatibility, and enhance stability.
Configuration Errors
Incorrect routing modes, disabled DHCP, or misconfigured WAN settings can block internet access.
Handling IP Address Conflicts
What Causes IP Conflicts
Multiple devices assigned the same IP address can disrupt connectivity.
Symptoms of Conflict
Intermittent connection loss or internet failure on specific devices.
Resolving Conflicts
Restarting devices or adjusting router DHCP settings usually resolves the issue.
Diagnosing ISP-Side Problems
Line and Signal Issues
Physical line damage, signal degradation, or authentication failures can block internet access.
Modem Authentication Failures
If the modem fails to authenticate with the ISP, Fix WiFi Connected may remain active without internet.
When to Contact Support
If all local troubleshooting fails, ISP intervention is necessary.
Resetting Network Settings on the Device
What Network Reset Does
It removes saved networks, resets adapters, and restores default configurations.
When to Use This Option
Use it after exhausting simpler troubleshooting steps.
Reconnecting After Reset
Reconnect to Fix WiFi Connected and re-enter credentials carefully.
Dealing with Public and Office Fix WiFi Connected Limitations
Captive Portals
Some networks require login confirmation before granting internet access.
Network Restrictions
Office networks may block certain services or require device authorization.
Acceptable Use Policies
Understanding network rules helps avoid false troubleshooting conclusions.
Preventing Fix WiFi Connected but No Internet Issues
Regular Router Maintenance
Restart routers periodically to maintain stability.
Keep Firmware and Drivers Updated
Updated software reduces compatibility and security issues.
Avoid Overloading the Network
Too many devices or heavy usage can overwhelm network resources.
Understanding the Problem as a Layered Failure
The Network Stack Perspective
Internet access depends on multiple layers working together.
Logical Troubleshooting Approach
Start from physical connections, move to software, then configuration.
Avoiding Random Fix Attempts
Structured troubleshooting saves time and reduces frustration.
Conclusion
The “Fix WiFi Connected but no internet” problem is not a contradiction, but a clear signal that the local wireless connection is functioning while external connectivity has failed. By understanding how Fix WiFi Connected, routers, DNS, devices, and ISPs interact, the issue becomes far less mysterious and far more manageable.
This guide has demonstrated that fixing this problem requires observation, patience, and logical progression rather than guesswork. In most cases, the solution lies in simple actions such as restarting equipment, correcting network settings, or updating drivers. In others, deeper configuration or ISP support is required.
Stable internet access is the result of many systems working in harmony. When one fails, the connection breaks. With the knowledge provided in this article, you now have the tools to identify the failure point, apply the right Fix WiFi Connected, and restore reliable connectivity with confidence.